Equilibrium of rigid
bodies: Part 3
Two-force and
three-force members:
|
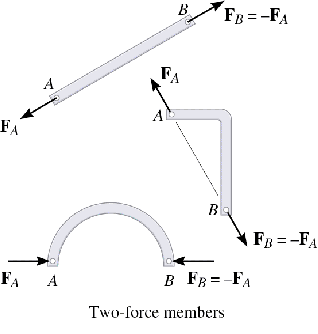
Examples of Two-Force Members are shown in the figure. For two-force members we have:
Equilibrium requires that the forces in a two-force member be equal and in opposite directions. |
|
|
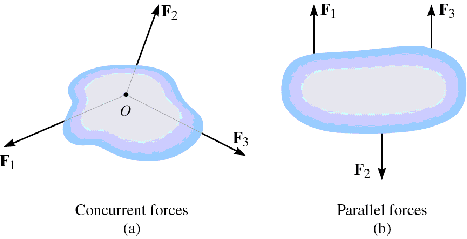
If member is subjected only to three forces, the forces should be either concurrent or parallel for member to be in equilibrium. |
|